Security Cluster Connectivity Is Generally Available on Azure Databricks

This is a collaborative post co-authored by Principal Product Manager Premal Shah, Microsoft, and Principal Enterprise Readiness Manager Abhinav Garg, Databricks
We're excited to announce the general availability of Secure Cluster Connectivity (also commonly known as No Public IP) on Azure Databricks. This release applies to Microsoft Azure Public Cloud and Azure Government regions, in both Standard and Premium pricing tiers. Hundreds of our global customers including large financial services, healthcare and retail organizations have already adopted the capability to enable secure and reliable deployments of the Azure Databricks unified data platform. It allows them to securely process company and customer data in private Azure Virtual Networks, thus satisfying a major requirement of their enterprise governance policies.
Secure Cluster Connectivity overview
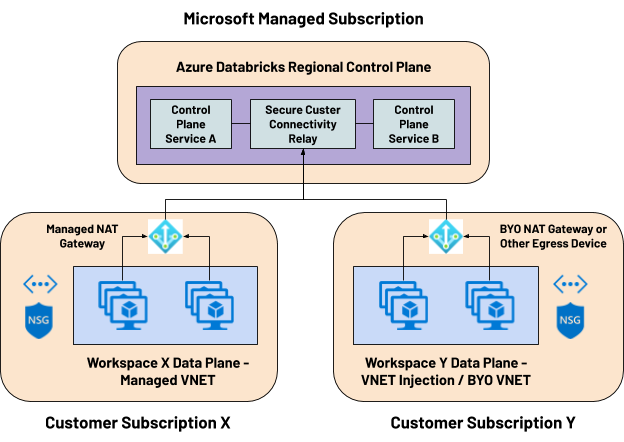
An Azure Databricks workspace is a managed application on the Azure Cloud enabling you to realize enhanced security capabilities through a simple and well-integrated architecture. Secure Cluster Connectivity enables the following benefits:
- No public IPs: There are no Public IP addresses for the nodes across all clusters in the workspace, thus eliminating the risk (or perception of it) of any direct public access. The two subnets required for a workspace are thus both private.
- No open inbound ports: There are no open inbound ports for access from the Control Plane or from other Azure services in the Network Security Group of the workspace. All access from a cluster in the data plane is either outbound (see minimum required) or internal to the cluster. The outbound access includes the connectivity to the Secure Cluster Connectivity relay hosted in the control plane, which acts as the transit for all cluster administration tasks and for running the customer workloads. An egress device with a public IP address is needed per workspace for all such outbound traffic.
- Increased reliability and scalability - Your data platform becomes more reliable and scalable for large and extra-large workloads, as there’s no dependency to launch as many public IPs as cluster nodes and attaching those to the corresponding network interfaces.
At a high-level, the product architecture consists of a control/management plane and data plane. The control plane resides in a Microsoft-managed subscription and houses services such as web application, cluster manager, jobs service, etc. The data plane that is in the customer’s subscription consists of the Virtual Network (two subnets), Network Security Group and a root Azure storage account known as DBFS.
You can deploy a workspace with Secure Cluster Connectivity using both Managed-VNET or VNET Injection (also known as Bring Your Own VNET) modes, either using the Azure Portal or any of the common automation options like ARM Templates, Azure CLI, etc.
- With the default Managed-VNET deployment, a managed Azure NAT Gateway will be deployed as the default egress device for the workspace and will be attached to the managed subnets.
- With the VNET Injection deployment, you should bring your own egress device, which could be your own-managed Azure NAT Gateway, Azure Firewall or a third-party appliance. You could also opt for a managed-outbound load balancer option for simpler deployments.
Gartner®: Databricks Cloud Database Leader
Getting started with Secure Cluster Connectivity
Get started with the enhanced security capabilities by deploying an Azure Databricks workspace with Secure Cluster Connectivity enabled using Azure Portal or ARM Template. Please refer to the following resources:
- Secure Cluster Connectivity Documentation
- Data exfiltration protection architecture and Securely access Azure Data Sources - both could be setup / configured alongside Secure Cluster Connectivity.
- Azure Databricks Security Best Practices
Please refer to Platform Security for Enterprises and Azure Databricks Security Baseline for a deeper view into how we bring a security-first mindset while building our popular first-party Azure service.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Product
November 21, 2024/3 min read