Serving Up a Primer for Unity Catalog Onboarding
Distill UC concepts in simple digestible nuggets to provide a path to adoption by laying out typical access patterns

Introduction
This blog is part of our Admin Essentials series, where we'll focus on topics important to those managing and maintaining Databricks environments. See our previous blogs on Workspace Organization, Workspace Administration, and Cost-Management best practices!
A big concern of any data platform is around data and user management, balancing the need for collaboration without compromising security. Previous blogs discussed the various strategies that an admin persona employs for data isolation by workspaces and best practices around workspace management, and introduced some of the core administrator roles.
Taking a journey down memory lane, on-prem data centers hosted clusters that were treated as precious commodities that took a while to set up correctly and were persistent. With the move to the cloud,the ability to create clusters at will to suit different use case needs became a simple exercise leading to the rise of ephemeral clusters - on demand clusters created for the duration of the workload.
A workspace is a logical boundary for a Line of Business (LOB) / Business Unit (BU), use case, or team to function that offers a balance of collaboration and isolation. Thanks to automation, the workspace creation has now been simplified to a few minutes! Users can be part of different workspaces depending on the various use cases they contribute to. More importantly, their privileges to data assets, irrespective of the workspace they belong to, remain the same. This allows organizations to adopt a centralized governance model that allows data access to be defined in a central location and users themselves should be free to be assigned and unassigned from workspaces, which can also get created and dissolved at will. This provides opportunities to manage complexity by reducing the proliferation of workspaces/clusters as a mechanism to segregate data.
In this blog, we want to show a simple customer journey of onboarding an organization to Unity Catalog (UC) and Identity Federation to address this need for centralized user and privilege management. We would like to prescribe a simple recipe to aid that process. This recipe can then be automated using the API, CLI, or Terraform to rinse-repeat and scale.
Refer to the recipe booklet worksheet to follow along.
Introducing the chefs
Let's first introduce all the chefs in the kitchen. Any SaaS-based product cannot live in isolation and needs to integrate well with existing tools and roles in your organization. The Cloud Admin and Identity Admin are roles that exist outside Databricks and need to work closely with the Account Admin role (a role that exists within Databricks), to achieve specific goals that are part of the initial setup. We will talk later about how these roles work together.
Non-Databricks Personas
| Cloud Admin | Cloud Admins can administer and control cloud resources that Unity Catalog leverage: storage accounts/buckets, IAM role/service principals/Managed Identities. |
| Identity Admin | Identity Admins can administer users and groups in the IdP, which provides the identities to the account level. SCIM connectors and SSO require setup by Identity Admin in the Identity Provider. |
Now let's focus on the chefs or personas that manage resources within Databricks. In addition to the core admin roles we introduced in the Workspace Administration blog, we will add additional roles called Catalog Admin, Schema Admin and Compute Admin. Some organizations might choose to go even more granular and create Schema Admins. The beauty of the Privilege Inheritance Model is that you can go as broad or fine as needed to suit your organization's needs.
Databricks hat - administrator personas
| Persona | Databricks' In-built Role? | Custom Group Recommended? |
|---|---|---|
| Account Admin | Y | Y |
| Metastore Admin | Y | Y |
| Catalog Admin | N | Y |
| Schema Admin | N | Y |
| Workspace Admin | Y | Y |
| Compute Admin | N | Y |
You will notice that we recommend creating a custom group even when there is an in-built role. This is a general best practice to encourage the use of groups, which makes it far easier to scale when it comes to managing entitlements across business units, environments, and workspaces. You could also re-use some of these groups that may already exist in your IdP and sync them with Databricks, allowing for centralized group organization while still retaining the ability to create groups at the Databricks account level for more granular access. Another important concept to understand is that the principal that creates a securable object becomes its initial owner, and the transfer of ownership to the appropriate group for a securable object, at any level, is possible and recommended.
Ingredients & tools
In this section, we'll list the utensils and tools for executing the UC recipe.
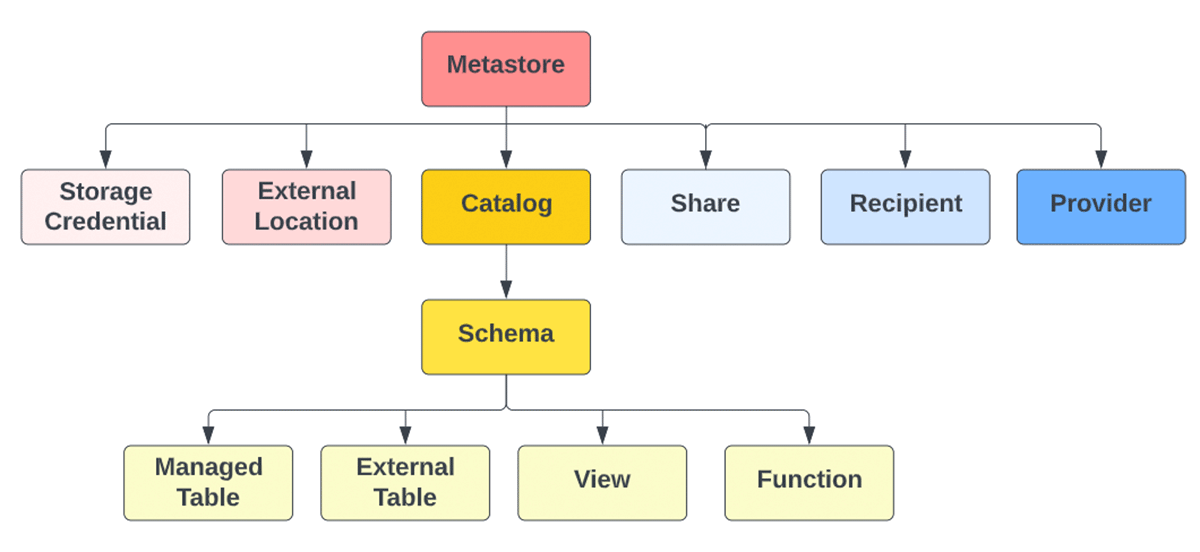
Refer to the Ingredients & Tools page in the Worksheet for detailed definitions.
Mise en place
Next we will go over a checklist to ensure that adequate groundwork has been completed and the appropriate personnel are lined up in preparation for UC onboarding.
| Collaborate with Identity Admin; Identify Admin Personas |
|
|---|---|
| Task | Persona |
| Set up SCIM from IDP | Account Admin (+ Identity Admin) |
| Set up SSO | |
| Identify Core Admin Personas (Account, Metastore, Workspace) |
|
| Identify Recommended Admin Personas (Catalog, Compute, Schema) |
|
| Collaborate with Cloud Admin; Create Cloud Resources |
|
|---|---|
| Task | Persona |
| Create Root bucket | Account Admin (+ Cloud Admin) |
| Create IAM role (AWS) Create Access Connector Id (Azure) |
|
Division of Labor
To deliver a nutritious meal, UC requires close collaboration and handoffs between multiple administrators. Once the recipe is understood, the cooking steps can be streamlined by utilizing automation.
Refer to the Division of Labor page in the Worksheet to understand who plays what role in the Administration of the Platform as part of the shared responsibility model.
Cooking steps
The following core steps require the collaboration of several admin personas with different roles and responsibilities and need to be executed in the following prescribed order.
| Master Checklist - Cooking Steps | ||
|---|---|---|
| Task | Notes | |
| 1 | Create a Metastore | Create 1 metastore per region per Databricks account |
| 2a | Create Storage Credentials | (optional) Needed if you want to access existing cloud storage locations with a cloud IAM role / Managed Identity to create external tables |
| 2b | Create External Locations | (optional) Needed if you have existing cloud storage locations you want to register with UC to store external tables |
| 3a | Create Workspace | (optional) Needed if you have no existing workspace |
| 3b | Assign Metastore to workspace | This step turns on Identity Federation as a feature |
| 3c | Assign Principals to workspace | This step is how Identity Federation is executed. Principals exist centrally and are "assigned" to workspaces |
| 4 | Create Catalog | Create catalogs per SDLC and/or BU needs for data separation |
| 5 | Assign Privileges to Catalog | Use Privilege Inheritance Model to manage GRANTS easily from the Catalog to lower levels |
| 6 | Assign Share Privileges on Metastore | (optional) This is part of Managed Delta Sharing which uses UC for managing privileges for Data Sharing |
Refer to the Cooking Steps page in the Worksheet for detailed execution steps.
Recipes to match your guest's palate
We will go over a few example scenarios to demonstrate how users across workspaces collaborate and how the same user has seamless access to data they are entitled to, from different workspaces. Line Of Business(LOB) / Business Unit(BU) are often used as an isolation boundary. Another commonly used demarcation is by environments for development/sandbox, staging and production.
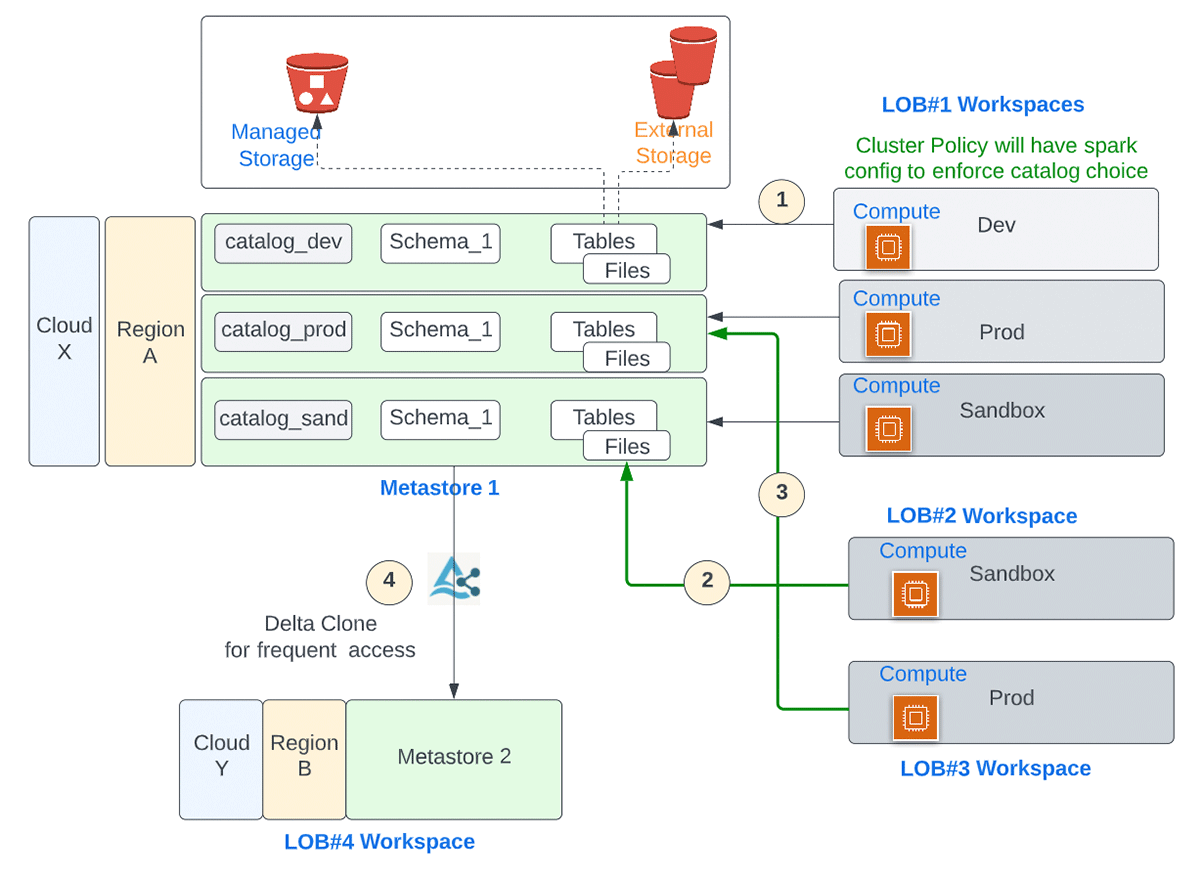
| Scenario | Problem Statement |
|---|---|
| LOB#1 |
|
| LOB#2 |
|
| LOB#3 |
|
| LOB#4 |
|
Refer to the Scenario Examples page in the Worksheet for detailed steps.
Served dish
Unity Catalog simplifies the job of an administrator (both at the account and workspace level) by centralizing the definitions, monitoring, and discoverability of data across the metastore, and making it easy to securely share data irrespective of the number of workspaces that are attached to it. Utilizing the Define Once, Secure Everywhere model has the added advantage of avoiding accidental data exposure in the scenario of a user's privileges inadvertently misrepresented in one workspace which may give them a backdoor to get to data that was not intended for their consumption. All of this can be accomplished easily by utilizing Account Level Identities and Managing Privileges. UC Audit Logging allows full visibility into all actions by all principals at all levels on all securables.
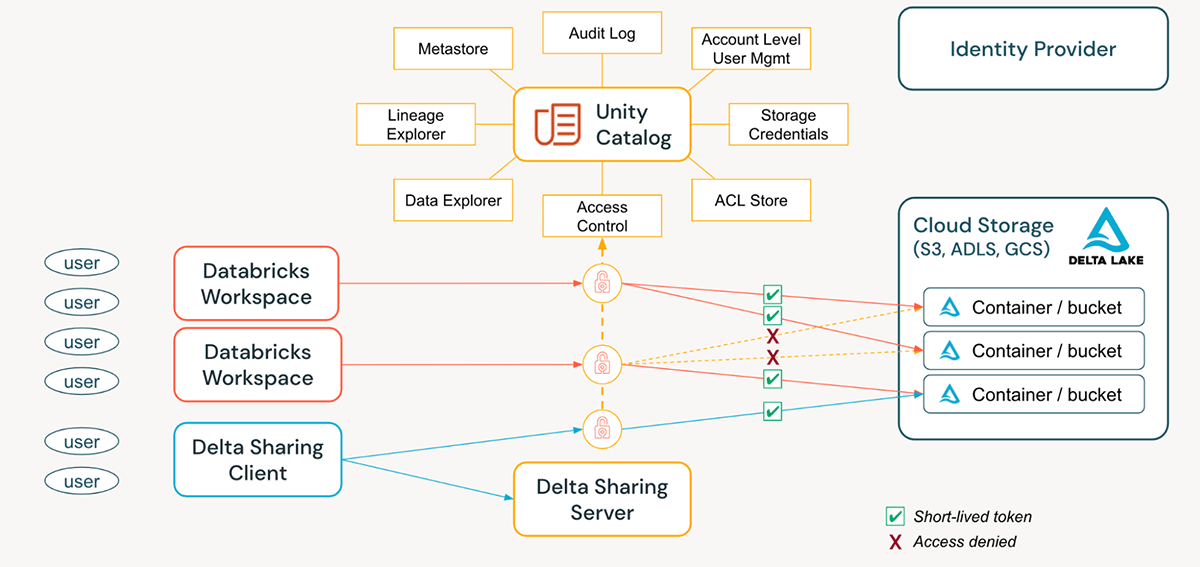
Additional tips
These are our recommendations for a more flavourful experience!
- Organize your chefs
- Set up SCIM & SSO at the Account Level
- Create Catalogs by SDLC environment scope, by business unit, or by both.
- Design Groups by business units/data teams and assign them to the appropriate workspaces (workspaces are conceptually ephemeral)
- Consider the number of members necessary in each of the Admin groups
- Delegate to your sous chefs
- Ensure that Account Admin, Metastore Admin, Catalog Admin, and Schema Admin understand the responsibilities appropriate to their roles
- Always make Groups, not individuals, the owner of Securables, especially Metastore(s), Catalog(s) and Schema(s)
- Combine the power of the Privilege Inheritance Model with the ability to 'Transfer Ownership' to democratize data ownership
- A well-governed platform involves a shared administrative burden across these various roles and automation is key to building a repeatable pattern while offering retaining control
- Automate to keep the kitchen line moving
- We've provided the recipe for a simple onboarding process, but as you scale to more users, groups, workspaces, and catalogs, automation becomes imperative. The plethora of options includes API, CLI, or the end-to-end guide provided by our Terraform Provider (AWS, Azure)
- Migrate to a more sophisticated palate
- Audit to keep the kitchen clean
Happy Cooking!
P.S: Hope we timed this right. Happy Thanksgiving.

