Building Databricks Apps with React and Mosaic AI Agents for Enterprise Chat Solutions

Databricks Apps provide a robust platform for building and hosting interactive applications. React is great for building modern, dynamic web applications that need to update smoothly and look polished. By combining this platform with a React-based frontend and Mosaic AI Agent Framework, developers can create efficient and intelligent chat applications.This blog focuses on the technical implementation of a Databricks-hosted chatbot and demonstrates its potential with an industry-specific Manufacturing Operations Management Chatbot use case.
Databricks Apps and Mosaic AI Integration
The architecture overview:
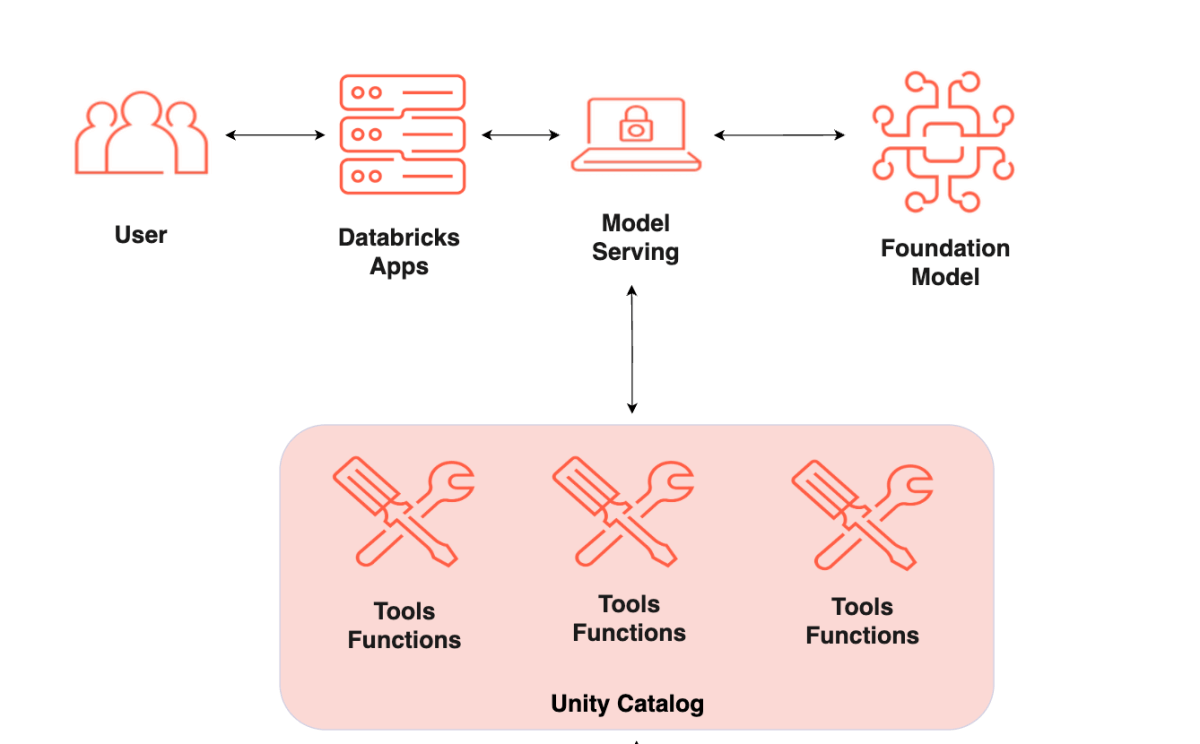
Core Strengths of Databricks Apps
Databricks Apps natively integrate with:
- Databricks SQL: For querying large datasets efficiently.
- Unity Catalog: For centralized data governance and access control.
- Model Serving: For deploying machine learning models at scale.
- Serving Endpoints: For efficient queries to the ML models and LLM agents.
- Jobs: For ETL pipelines and workflow processes.
Databricks Apps eliminate the need for external hosting infrastructure. Applications inherit the platform's built-in security, compliance, and resource management features, streamlining deployment and maintenance.
Databricks Apps support a wide range of frameworks such as Dash, Streamlit, Gradio, Flask, and FastAPI. This flexibility allows for both data-rich and visually engaging applications.
What is Mosaic AI Agent Framework?
The Mosaic AI Agent Framework is a set of tools on Databricks that helps developers create, deploy, and manage AI agents, such as those used in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). It integrates with frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex and uses Databricks features like Unity Catalog for data governance and tool-calling.
Developers can log and test agents with MLflow, debug their behavior, and enhance performance. Features like request logging, response token streaming, and review apps make building and deploying AI agents easier for real-world use cases.
Use Case: Manufacturing Operations Management Chatbot
Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) is crucial for optimizing production processes, improving efficiency, and maintaining competitiveness in today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
The demand for operation management using AI agents with natural language interfaces is rapidly growing, driven by the need for increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and enhanced user experiences.
According to the latest publication from Meticulous Research® (source), the AI in manufacturing market is projected to reach $84.5 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 32.6% during the forecast period 2024–2031 [1]. This significant growth underscores the increasing recognition of the importance of AI-driven operation management in various industries.
A manufacturing company implementing the Mosaic AI chatbot leveraging tool-calling can assist production managers in:
Bottleneck Analysis
- Tool function: Queries Databricks SQL using the
identify_bottleneck_stationfunction to determine the station causing the most delays. - Example query: "What’s the current bottleneck in the assembly line?"
- Response: "Station 5 is the current bottleneck, with an average delay of 15 minutes per cycle."
Inventory Tracking
- Tool function: Calls
check_inventory_levelsto retrieve real-time stock data for a specified station. - Example query: "Do we have enough materials for Station 3?"
- Response: "Station 3 has enough materials for the next five production cycles.”
These queries can be easily implemented as functions stored in Unity Catalog, using either SQL or Python. Then an AI agent can perform tasks such as data retrieval, code execution, and context-based decision-making by leveraging the function calls. While we won’t dive into the specifics of setting up the agent for tool-calling here, you can refer to the Databricks Generative AI Cookbook here for detailed guidance.
Once the Mosaic AI agent is set up and configured to handle various tools, it can be deployed as a model-serving endpoint on Databricks. This endpoint acts as the backend interface, allowing frontend applications like chatbots to send queries and receive real-time insights.
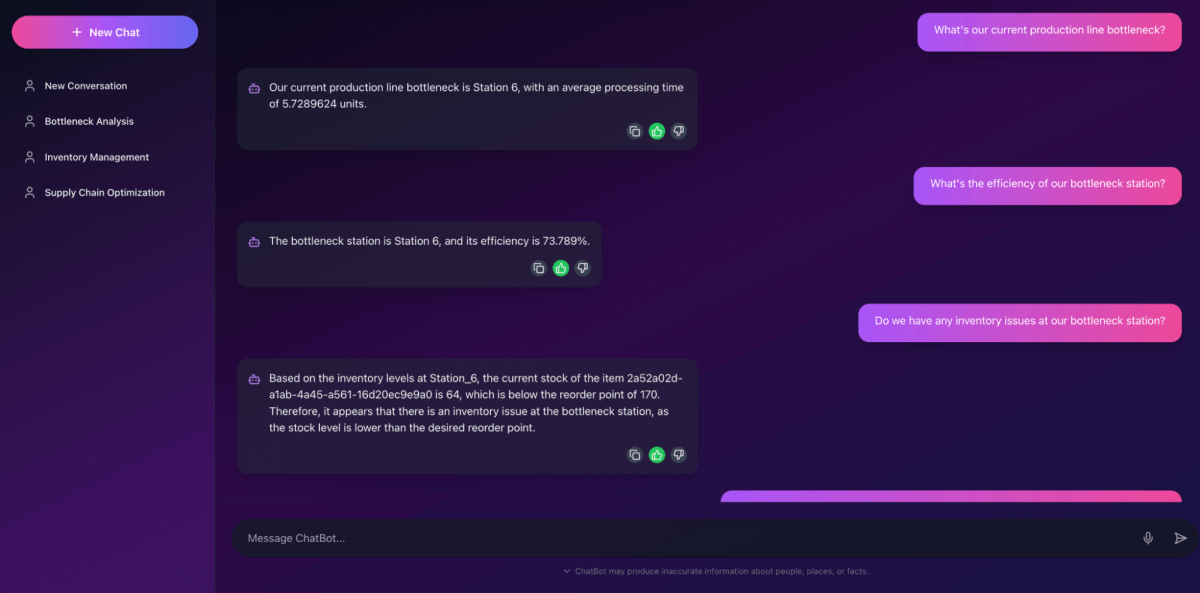
Here is the chatbot interface running locally; later, we will demonstrate it after deployment to Databricks Apps.
Databricks Apps Implementation
1. Frontend with React
The React frontend provides an interactive and user-friendly interface for querying the chatbot and visualizing responses. Core features include real-time message rendering, query submission, and bot response handling, interactive UI with feedback, and Markdown support.
Frontend Code Sending Messages to the Backend
API Client: Axios is used to make HTTP requests. The baseURL is dynamically set based on the environment (development or production).
HandleSendMessage: It captures user input, sends the message to the /api/chat API endpoint, and updates the chat history with both user and bot messages.
2. Backend with FastAPI
The FastAPI backend serves as the bridge between the React frontend and Mosaic AI agents. It routes user queries to the agent’s model-serving endpoint to get a response.
Backend Code Handling User Queries
This API endpoint receives user messages, interacts with the Mosaic AI agent model-serving endpoint, and returns task-specific responses.
In FastAPI, the order of mounting sub-applications is crucial because it determines how incoming requests are routed.
app.mount("/api", api_app):
- This mounts a sub-application (
api_app) at the/apiroute. - Any request starting with
/api(e.g.,/api/chat) is routed to this sub-application. - This ensures that all API-related requests are processed by the
api_appinstance.
app.mount("/", ui_app):
- This mounts the static files from the
client/builddirectory at the root (/) route. - This is typically used to serve the compiled frontend application, which include
index.html, JavaScript, CSS, and other static assets. Most of the major UI frameworks (e.g. React, Vue and Svelte) support compilation into such a set of assets via different bundlers (e.g. Vite, Webpack or esbuild). - Any request that does not start with
/apiwill be routed to theui_app.
- API Setup and Endpoint Definition: The code defines a FastAPI application with a POST endpoint (
/chat) under theapi_appinstance that points to the Mosaic AI agent's model-serving endpoint on Databricks. - Dependency Injection and Request Handling: The endpoint uses FastAPI's dependency injection mechanism (
Depends) to inject aWorkspaceClient, which is responsible for interacting with Databricks APIs. Thechat_with_llmfunction takes aChatRequestcontaining the user’s message, formats it as aChatMessagewith the roleUSER, and sends it to the serving endpoint using theclient.serving_endpoints.querymethod. - Response Parsing and Return: The response from the agent is structured and returned as a
ChatResponseto the client.
Deployment on Databricks Apps
1. Preparing the Backend
- Place the FastAPI code in an
app.pyfile. - Define dependencies in
requirements.txt: - Create an
app.yamlfile:
The command section outlines the gunicorn server configuration with the following specifications:
- server.app:app: Runs your FastAPI application.
- -w 2: Uses two worker processes to handle incoming requests.
- uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker: Uses Uvicorn workers, which are compatible with FastAPI's ASGI framework.
The env section specifies key-value pairs that define environment variables to pass to the app [2]:
- name: the name of the environment variable.
- valueFrom: For an externally defined value, the name of the source containing the value. For example, the name of a secret or a database table containing the value.
I am mapping the environment variables SERVING_ENDPOINT_NAME to the Databricks resource model-serving endpoint agent_MODEL_NAME_FQN, where MODEL_NAME_FQN represents the three-level namespace of Unity Catalog for catalog.db.model_name.
2. Preparing the Frontend
- Build the React app with
npm run buildand place the static files in/client/build.
Here is the file structure:
3. Deployment Steps
- Create the Databricks App:
- Configure Databricks Resources:
I am setting up the Databricks resources to align with the features defined in the env section of the app.yaml file. This includes configuring resources such as the model-serving endpoint (agent_MODEL_NAME_FQN).
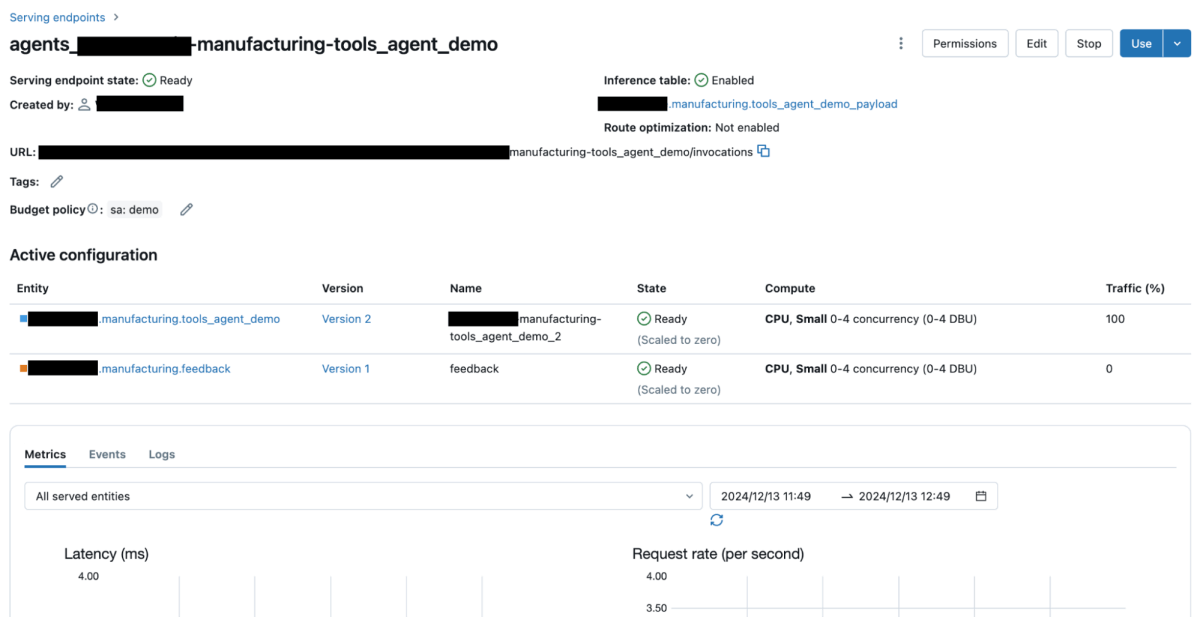
The below image shows that the chatbot app has been successfully created:
- Sync Files:
- Deploy the App:
After executing this command, the deployment process will take a few minutes. Once successfully deployed, the Databricks App's URL will be displayed, indicating that it is up and running.
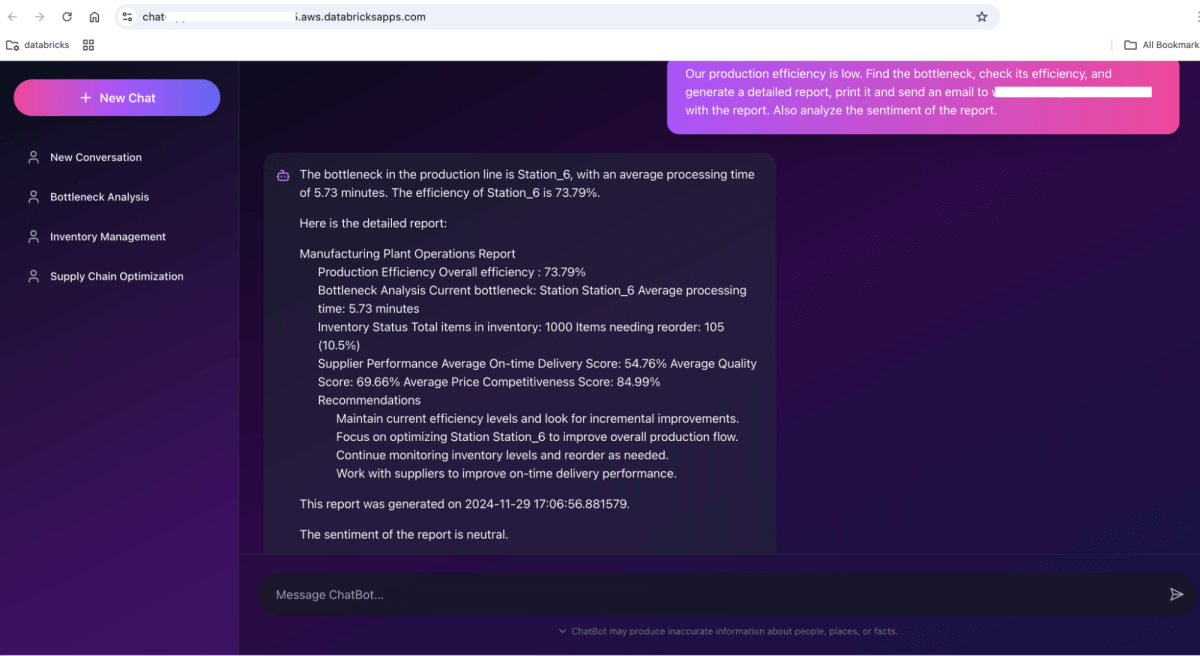
And you can start chatting with it. For example, our production efficiency is low. Find the bottleneck, check its efficiency, and generate a detailed report. Send an email to [email protected] with the report. Also analyze the sentiment of the report.
Conclusion
Integrating Databricks Apps with React and the Mosaic AI Agent Framework offers a powerful solution for creating dynamic, interactive chat applications. By leveraging Databricks' built-in data processing capabilities, secure model-serving, and streamlined deployment infrastructure, developers can build robust systems that handle complex queries.
The use of FastAPI as a bridge between the React frontend and Mosaic AI agents ensures seamless communication. While Databricks Apps support various Python backend frameworks such as Flask and Django, FastAPI was chosen for its concise and developer-friendly API.
This setup showcases how advanced AI capabilities can be integrated into practical industry solutions, such as manufacturing chatbots, to drive efficiency and decision-making. As Databricks continues to evolve its platform, these integrations can expand to cater to broader use cases, making it an essential tool for businesses aiming to innovate with AI-driven solutions.
To reference the source code, please find the GitHub repository linked here.
References:
[1] AI in Manufacturing Market to Reach $84.5 Billion by 2031. Source:
https://www.meticulousresearch.com/pressrelease/294/ai-in-manufacturing-market
[2] Databricks Apps configuration. Source:
https://docs.databricks.com/en/dev-tools/databricks-apps/configuration.html#databricks-apps-configuration
Integrating Databricks Apps with React and the Mosaic AI Agent Framework offers a powerful solution for creating dynamic, interactive chat applications. By leveraging Databricks' built-in data processing capabilities, secure model-serving, and streamlined deployment infrastructure, developers can build robust systems that handle complex queries.
Want to see it in action?
Try the Databricks Apps Product Tour to create the fastest and safest Data and AI applications on the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Manufacturing
October 1, 2024/5 min read
From Generalists to Specialists: The Evolution of AI Systems toward Compound AI
Product
November 27, 2024/6 min read