LLMs in the lakehouse: a quantum leap forward for the public sector

Over the past few months, interest in Large Language Models (LLMs) from Public Sector agencies has skyrocketed as LLMs are fundamentally changing the expectations that people have in their interactions with computers and data. From Databricks' point of view, practically every Public Sector customer and prospect we interact with feels a mandate to inject LLMs into their mission. We repeatedly hear questions about what LLMs (like Databricks' Dolly) are, what they can be used for, and how the Databricks Lakehouse will support LLM-related applications. In this post, we will touch on these questions in the context of the unique needs, opportunities and constraints of Public Sector organizations. We will also focus on the benefits of creating, owning and curating your own LLM vs adopting a technology that requires third party data sharing like ChatGPT.
What are LLMs?
Today's LLMs represent the latest version in a series of innovations in natural language processing, starting roughly in 2017 with the rise of the transformer model architecture. These transformer-based models have long possessed uncanny abilities to understand human language well enough to accomplish tasks such as identifying sentiment; extracting named people, places and things; and translating documents from one language to another. They have also been capable of generating interesting text from a prompt, with varying degrees of quality and accuracy. More recently, researchers and developers have discovered that very large language models, "pre-trained" on very large and diverse sources of text, can be "fine-tuned" to follow a variety of instructions from a human to generate useful information.
Previously, the best practice was to train separate models for each language-related task. The model training process required resources: curated data, compute (typically one or more GPUs), and advanced data science and software development expertise. While such models can be highly accurate, there are clearly resource constraints - both in terms of computation and human effort - when scaling up their usage. With the rapid rise of ChatGPT to stardom, we now see that a single LLM - with the appropriate amount of context and the right prompt - can be used to deliver on many different tasks, sometimes with better accuracy than a more specialized model. And the LLMs' ability to generate new text - "Generative AI" - is both fascinating and extremely useful.
What can LLMs be used for in the Public Sector?
Private sector organizations have reported amazing benefits from LLMs, such as code generation and migration, automated customer feedback categorizations and responses, call center chatbots, report generation, and much more. As a microcosm of many different industries, Public Sector agencies have the same LLM opportunities, in addition to other unique needs. Common Public Sector use cases include:
- Regulatory compliance assistance. With its ability to interpret and process text, an LLM can assist in determining compliance requirements by analyzing regulatory documents, legal texts, and relevant case law. It can help government agencies and businesses understand the implications of regulations and ensure adherence to the law.
- Training and education assistant. Scale and accelerate learning for students by serving as a virtual instructor, answering questions, explaining complex concepts, retrieving relevant portions of lecture recordings, or recommending course catalog offerings.
- Summarizing and answering questions from technical documents. Perhaps the most ubiquitous LLM-related use case in the Public Sector is to extract knowledge from thousands or millions of documents, including PDFs and emails, into a format conducive to quickly finding relevant content based on search criteria, then use the relevant content to generate summaries or reports.
- Open-source intelligence. LLMs can greatly enhance the Intelligence Community's analysis of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) by processing and analyzing vast amounts of publicly available multilingual information. LLMs can extract key entities, relationships, sentiments, and contextual understanding from diverse sources such as social media, news articles, and reports, then efficiently summarize and organize this information, aiding analysts in rapidly comprehending and extracting insights from large volumes of OSINT data.
- Modernizing legacy code bases. Government agencies continue to move data workloads off of mainframes, on-premise data warehouses, and proprietary analytics software. By putting coding assistants in the hands of developers and analysts to suggest code as they go, or training custom LLMs to handle bulk code conversion, the pace of migration can accelerate while knowledge workers gracefully acquire relevant software skills.
- Human resources. As the nation's largest employer, the Federal government faces unique challenges in hiring and ensuring employee satisfaction. Leveraging LLMs in the HR field can help address these challenges by automating resume screening, matching candidates to job descriptions, and analyzing employee feedback to improve hiring processes and enhance workforce engagement. Additionally, LLMs can assist in ensuring HR policy compliance, supporting diversity and inclusion initiatives, and providing personalized onboarding and career development recommendations.
How will Databricks support the needs of Public Sector organizations in a world powered by LLMs?
While certainly powerful, LLMs also introduce a new set of challenges that is amplified by some of the operating constraints native to Public Sector organizations. Let's dissect a few of these and align them with the Databricks Lakehouse capabilities:
Challenge #1: Data sovereignty and governance
The challenge
Most Public Sector organizations have strict regulatory controls around their data. These controls exist for privacy, security, and the need to preserve secrecy in some cases. Even the simple task of asking an LLM a question or set of questions could reveal proprietary information. Furthermore, most Federal agencies will have the need to fine-tune LLMs to meet their particular requirements. For these reasons, it's logical to assume that Public Sector agencies will be limited in their use of public models. It's likely that they'll require the models to be fine-tuned in an environment that ensures their confidentiality and security, and that interactions with the models via various prompting methods are also confidential.
Databricks' solution
Databricks' Lakehouse platform has the tools necessary to develop and deploy end-to-end LLM applications. (More on that later.) Moreover, Databricks possesses the necessary certifications to process data for the vast majority of U.S. Public Sector organizations. Databricks is a trusted and capable partner for organizations seeking to harness the full power of LLMs without the risks that come from leveraging proprietary LLMs-as-a-service like ChatGPT or Bard.
Beyond Databricks, the industry is seeing increased evidence that open-source LLMs - used appropriately - can deliver results that approach parity with the leading proprietary LLMs. The evidence is strongest in use cases where the proprietary LLMs must understand nuanced context or instructions on which they have not previously been trained. In these cases, open-source LLMs can be either prompted with or fine-tuned on organization-specific data to deliver astounding results. In this solution architecture, organizations can achieve world-class results with modest amounts of compute and development time, without data ever leaving approved boundaries. For Public Sector organizations, this represents a significant advantage that cannot be overlooked.
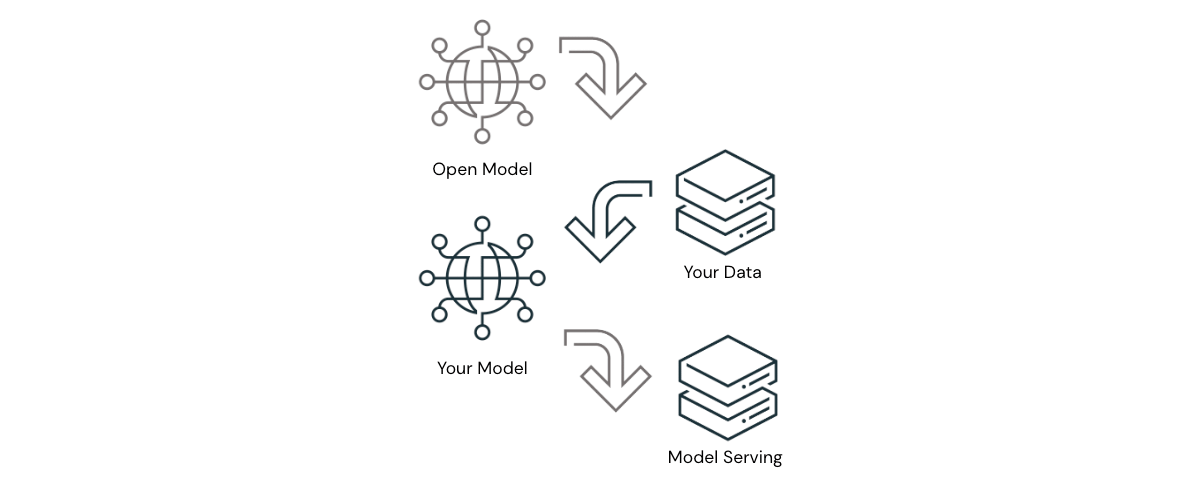
Databricks' belief in the power of open-source LLMs is reinforced by our releasing Dolly 2.0, the first open source, instruction-following LLM, fine-tuned on a human-generated instruction dataset licensed for research and commercial use. Dolly's release has been followed by a wave of other capable open-source LLMs, some of which have very impressive performance. Databricks strives to give Public Sector organizations a platform to build applications with their LLM of choice - open-source, or commercial - and we are excited for what's yet to come.

Challenge #2: Architectural complexity
The challenge
Data estate modernization continues to be top of mind for most technical leaders in the Public Sector. Mostly gone are the days of on-premise data warehouses, typically replaced by a data warehouse or lakehouse in the cloud. Organizations that have not yet migrated to the cloud - or that opted for a data warehouse in the cloud - now face another inflection point: how to adopt LLMs in an architecture that can't accommodate them? Given the immense potential of LLMs to impact agencies' missions and the public servants delivering on them, it is critical to establish a future-proof architecture. Enter the lakehouse.
Databricks' solution
Databricks has long been a capable home for machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) workloads. Customers have been using production-grade LLMs and their predecessors on Databricks for years, taking advantage of features such as:
- Scalable compute for preprocessing of unstructured data like text, images and audio
- Access to the full suite of open-source ML/AI libraries
- A native best-in-class notebook development environment, with excellent support for IDE integration as well
- Data governance capabilities via Unity Catalog that ensure proper access controls to
- Structured data (databases and tables)
- Unstructured data (files, images, documents)
- Models (LLMs or otherwise)
- GPU compute options for the training of and predictions from ML models - now a prerequisite for working with transformer-based LLMs
- End-to-end model lifecycle management with MLflow and Unity Catalog. Models are treated as first class citizens, with lineage to their source data and training events, and can be deployed in either batch or real-time mode
- Model serving capabilities, which become increasingly critical as organizations fine-tune, host and deploy their own LLMs
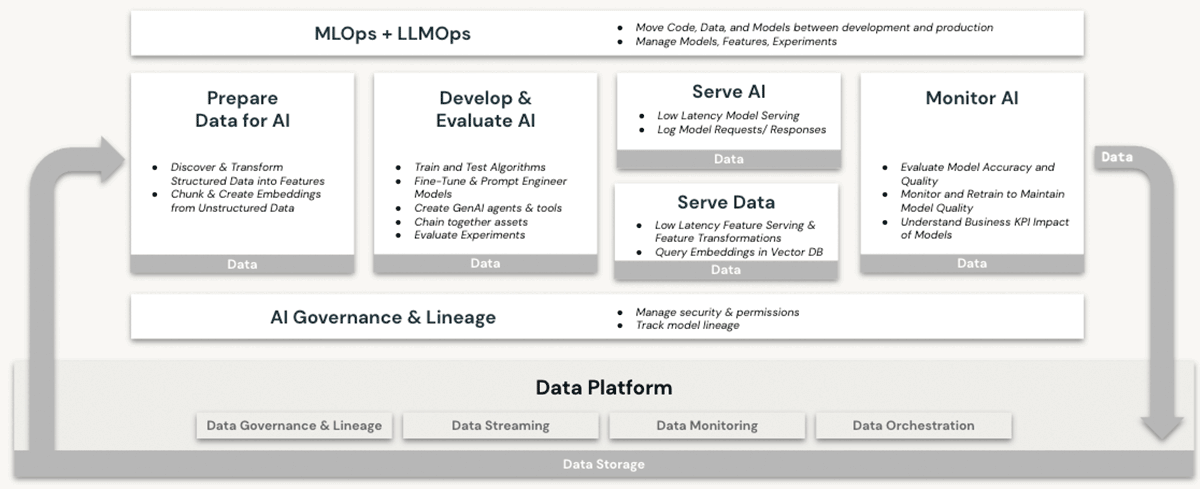
None of these features are offered in a data warehouse, even in the cloud. To use LLMs in conjunction with a data warehouse, an organization would need to procure other software services for all facets of the model training and deployment processes, and send data back and forth between these services. Only the Databricks Lakehouse architecture offers the architectural simplicity of performing all LLM operations in a single platform, fully delivering on the benefits explained in our discussion of data sovereignty above.
At Data and AI Summit 2023, Databricks presented Lakehouse AI, which adds several major new LLM-related features that significantly simplify the architecture for LLMOps, including:
- Vector Search for indexing. A Databricks-hosted vector database helps teams quickly index their organizations' data as embedding vectors and perform low-latency vector similarity searches in real-time deployments.
- Lakehouse Monitoring. The first unified data and AI monitoring service that allows users to simultaneously track the quality of both their data and AI assets.
- AI Functions. Data analysts and data engineers can now use LLMs and other machine learning models within an interactive SQL query or SQL/Spark ETL pipeline.
- Unified Data & AI Governance. Enhancements to the Unity Catalog to provide comprehensive governance and lineage tracking of both data and AI assets in a single unified experience.
- MLflow AI Gateway. The MLflow AI Gateway, part of MLflow 2.5, is a workspace-level API gateway that allows organizations to create and share routes, which then can be configured with various rate limits, caching, cost attribution, etc. to manage costs and usage.
- MLflow 2.4. This release provides a comprehensive set of LLMOps tools for model evaluation
Challenge #3: Skills gap
The challenge
Government agencies have struggled with a persistent "brain drain" in recent years, particularly in roles that overlap with hot technological trends such as cybersecurity, cloud computing, and ML/AI. The current intense focus on LLMs is driving even more demand for talented practitioners in ML/AI. Inevitably, the allure and perks that come with employment in big tech and the startup scene will exacerbate the talent shortage in the public sector. Government leadership needs access to platforms and partnerships that will help them to easily adopt LLMs and empower their employees to become self-sufficient with them.
Databricks' solution
Databricks is busy rolling out features that simplify and expand upon the existing capabilities to work with LLMs in the lakehouse platform. These include:
- Simplified patterns for using pre-trained LLMs from Hugging Face for inference tasks in data pipelines, or fine-tuning them for better performance on your own data in Databricks.
- Simplifying the process and improving the performance of loading data from Apache Spark into Hugging Face model training or fine-tuning jobs.
- Industry-specific LLM solution accelerators, showing repeatable implementation patterns for quick wins, such as customer service analytics and product discovery
- The MLflow 2.3 release, featuring native LLM support, in particular:
- Three brand new model flavors: Hugging Face Transformers, OpenAI functions, and LangChain.
- Significantly improved model download and upload speed to and from cloud services via multi-part download and upload for model files.
- A built-in Databricks SQL function allowing users to access LLMs directly from SQL. This feature can circumvent lengthy and complex language model development processes by allowing analysts to simply craft effective LLM prompts
- As announced at Data & AI Summit 2023,
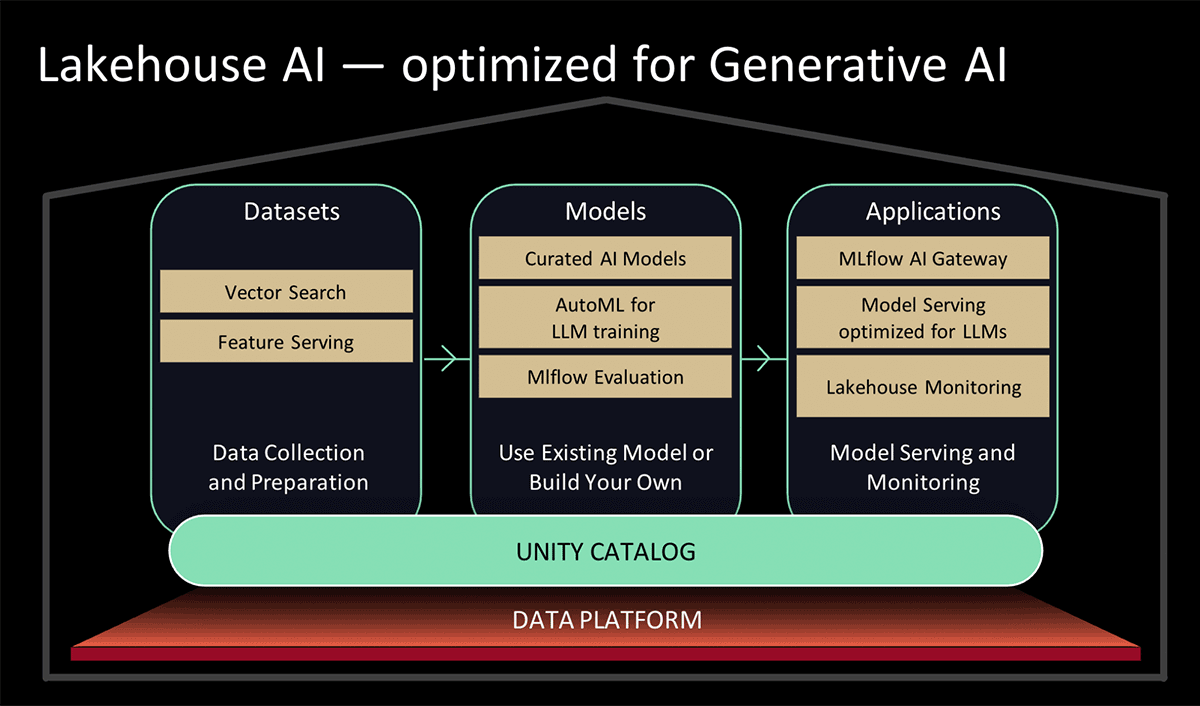
- Additions to Databricks' UI-based AutoML service that will fine-tune LLMs for text classification as well as embedding models; and
- Curated models, backed by optimized Model Serving for high performance. Rather than spending time researching the best open source generative AI models for your use case, you can rely on models curated by Databricks experts for common use cases.
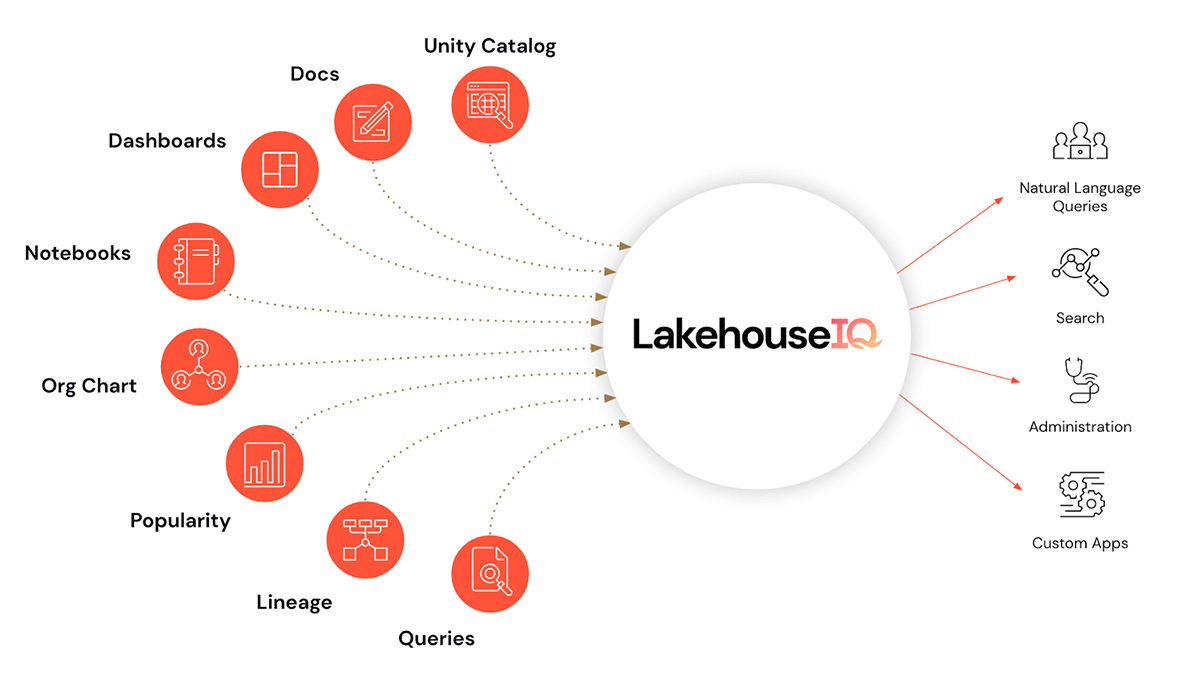
- And perhaps the icing on the cake, LakehouseIQ, a knowledge engine that learns the unique nuances of your business and data to power natural language access to it for a wide range of use cases.
In addition to making LLMs easy to use in Databricks, we are also introducing LLM training and enablement programs to help organizations scale up their LLM proficiency. These are delivered at a level that is approachable for Databricks' public sector users.
- Partnering with EdX to deliver expert-led online courses that are specifically focused on building and using language models in modern applications
Conclusions and next steps
Opportunities to harness LLMs to accelerate Public Sector use cases abound. Immense value remains buried in legacy data, just waiting to be discovered and applied to current problems. Come learn more about how Databricks can help you adopt LLMs in your mission by participating in our webinar Large Language Models in the Public Sector on August 2 at Noon, EDT. Also, peruse the feature preview signups listed in the Lakehouse AI announcement and see which ones your organization qualifies for.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Partners
February 22, 2024/4 min read
Strengthening Cyber Resilience through Efficient Data Management

Security and Trust
April 30, 2024/4 min read
