Multi-cloud Architecture for Portable Data and AI Processing in Financial Services
Meeting Stressed-Exit Regulatory Requirements and Managing Risk Successfully and Cost-Effectively with Databricks Lakehouse

Many financial institutions are developing a multi-cloud strategy to reduce operational risk, adhere to regulatory requirements, and also to benefit from a choice of cloud services and prices from multiple vendors.
In this blog post, we share an infrastructure blueprint for multi-cloud data processing with a portable multi-cloud architecture. Using a specific example, we show how the Databricks Lakehouse platform significantly simplifies the implementation of such an architecture, making it easier for organizations to meet regulatory requirements and reduce operational cost and risk.
The UK Bank of England and the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) have recently announced new regulations for systemically important banking and financial services industries (FSI). This requires them to have plans in place for “Stressed Exit” scenarios relating to services from third parties, such as cloud IT vendors:
- SS2/21 - Outsourcing and third party risk management
- SS4/21 - Ensuring operational continuity in resolution
These regulations focus on ensuring business continuity during changes to service providers, including cloud services. There is an onus on the FSI firms to demonstrate how operational arrangements supporting critical services can be maintained in the event that services are changed to a different provider.
Although these regulations are UK-specific, international banks and other FSI companies will need to cater for these regulations if they want to do business in the UK. Also, there is a possibility that this type of regulatory model will be adopted in other jurisdictions in the future (similar requirements are currently being discussed in other markets such as ASEAN)
Global FSI companies need to have a strategy to future-proof their cloud architecture for:
- Regulatory changes requiring a multi-cloud solution in the future
- Operational risk of a cloud vendor changing its pricing model or service catalog
- Operational risk of a cloud vendor deciding to withdraw from a geographic region
- Geo-political change requiring a move from cloud to on-premises in a particular geographical region.
There are three key requirements for achieving intra-cloud and hybrid-cloud (cloud to on-premises) portability:
- An open, portable data format and data-management layer with a common security model
- Foundation application services (such as database and AI processing) that are common between clouds and can also be deployed on-premises
- Open application development coding standards and APIs, allowing a single code-base to be shared between cloud-vendor and on-premises platforms
The Cloud Native Challenge
A typical approach for deploying data applications is to use cloud vendor native services. This was a common pattern in the initial stages of cloud adoption, with organizations picking a preferred cloud vendor for the majority of their workloads. However, as companies adopt a multi-cloud strategy this creates a set of challenges:
- Multiple codebases must be maintained to run a single application against multiple cloud-vendor native services
- Multiple cloud infrastructure builds must be maintained to support the build of the application in different cloud environments
- Multiple sets of cloud-service skills must be curated in the organization to ensure the application can be supported in all environments
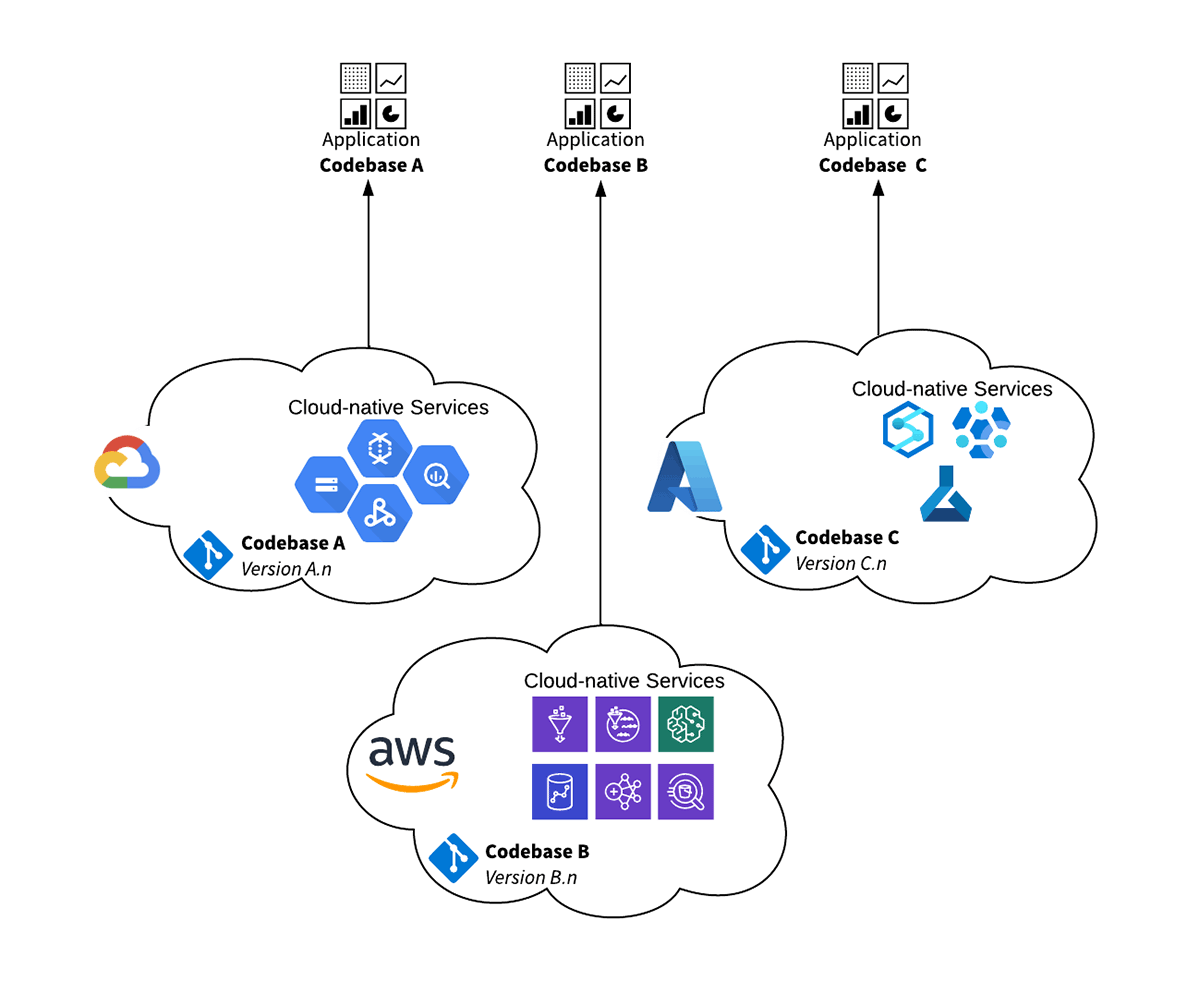
This approach becomes costly to manage and maintain through application release cycles and also evolving regulatory, geo-political and vendor service changes. The operational cost of maintaining multiple codebases for different systems with a common functional and non-functional requirement can become huge. Ensuring equivalent results and accuracy between codebases and also maintaining multiple skill-sets and infrastructure builds are a large part of the overhead.
In addition to this, many organizations end up building and operating another equivalent service to run in their own data-centers (on-premises) for classes of data that cannot be stored and processed in a third-party cloud vendor. This is typically due to local regulatory or client-sensitive data requirements that are specific to a geographic region.
We have recently seen an example of this situation at an international bank with a large presence in the UK. They have a requirement to run daily Liquidity Risk calculations on their primary strategic cloud vendor platform. The customer now has the challenge of maintaining equivalent functionality on a different cloud platform to satisfy regulatory requirements. The main challenges they face are the cost of maintaining two different code bases as well as achieving equivalent performance and matching results for both systems. Over time the code base for the primary application has been optimized and diverged from the secondary system to the point where a major project is required to realign them.
Blueprint For Multi-Cloud Data Processing
Here we present a standard blueprint for enterprise data processing that caters for a modern multi-cloud, multi-geography and multi-regulatory environment.
This is based on the following foundations:
- Open Data: data should be stored in an open, portable format, with a common access and processing interface for all clouds. This should also be available for vendor-independent on-premises deployments.
- Open API Standards: business applications access the data and data processing services using non-proprietary standardized interfaces and APIs. These should be commonly available across multiple cloud platforms and on-premises deployments.
- Code Portability: business logic code, ML / AI models and data synchronization services can be deployed in all the target cloud platforms and on-premises environments from a single code-branch without being re-factored.
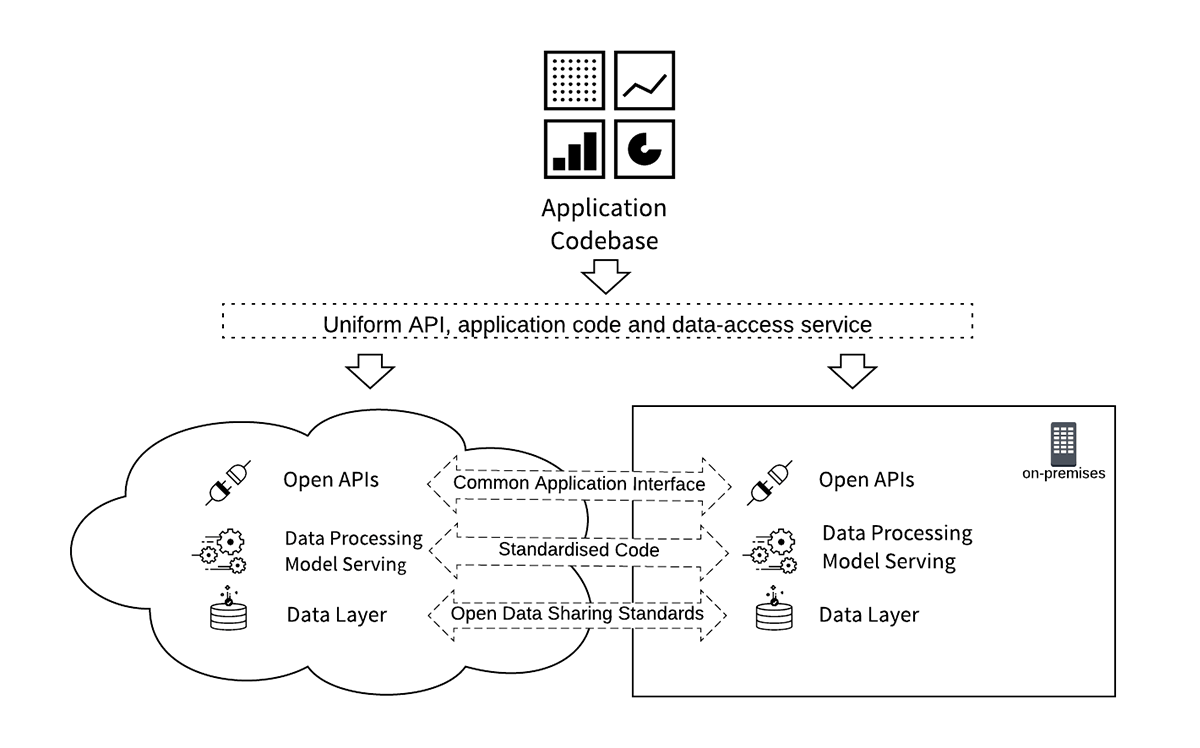
Using a data analytics architecture with APIs and data services that are standardized across different infrastructure platforms provides a simpler and cheaper solution. Operational cost is greatly reduced by having a single codebase while still retaining control of localized physical implementations to adhere to regulatory requirements across multiple geographies.
Databricks Solution for Hybrid Cloud Data Processing
Databricks’ Lakehouse Platform simplifies multi-cloud deployments with its open standards and open protocols approach, as it is closely aligned with the standard blueprint outlined above. Because the Lakehouse and its underlying open-source components provide a common functional interface across all clouds, a single codebase can operate against multiple cloud vendor environments.
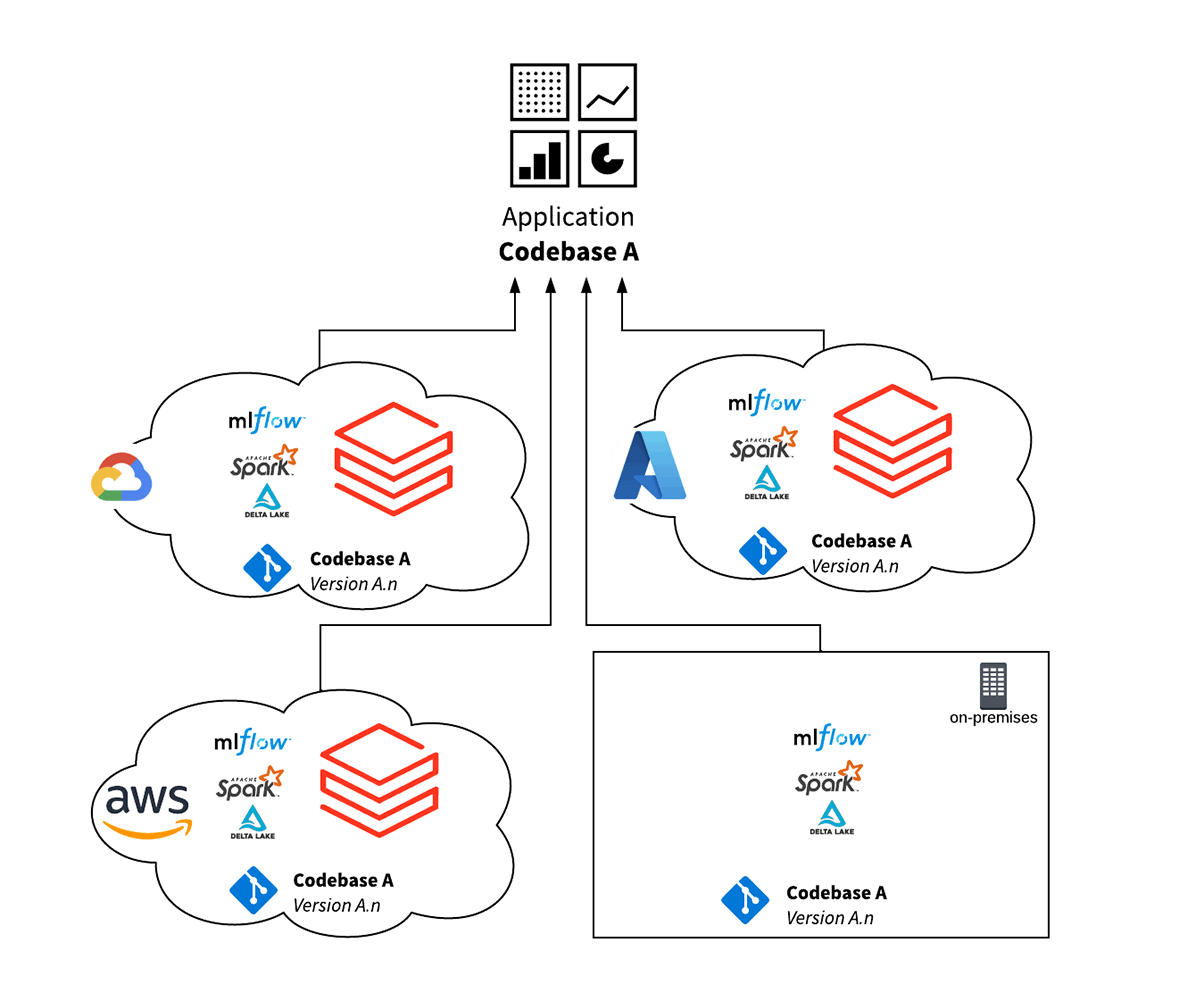
The features and benefits of this design are:
- Delta Lake provides a high performance open standards data layer, allowing for frictionless data interoperability and portability between environments. This also simplifies data reconciliation and integrity checks across environments.
- A single code base for multiple cloud infrastructures lowers the cost of operations and testing, enabling developers to focus on feature development and code optimization, instead of keeping environments in-sync.
- The Databricks stack is based on open-source non-proprietary standards, which means that a wider skills-base is available to develop and maintain the codebase. This reduces the cost of implementation and operation.
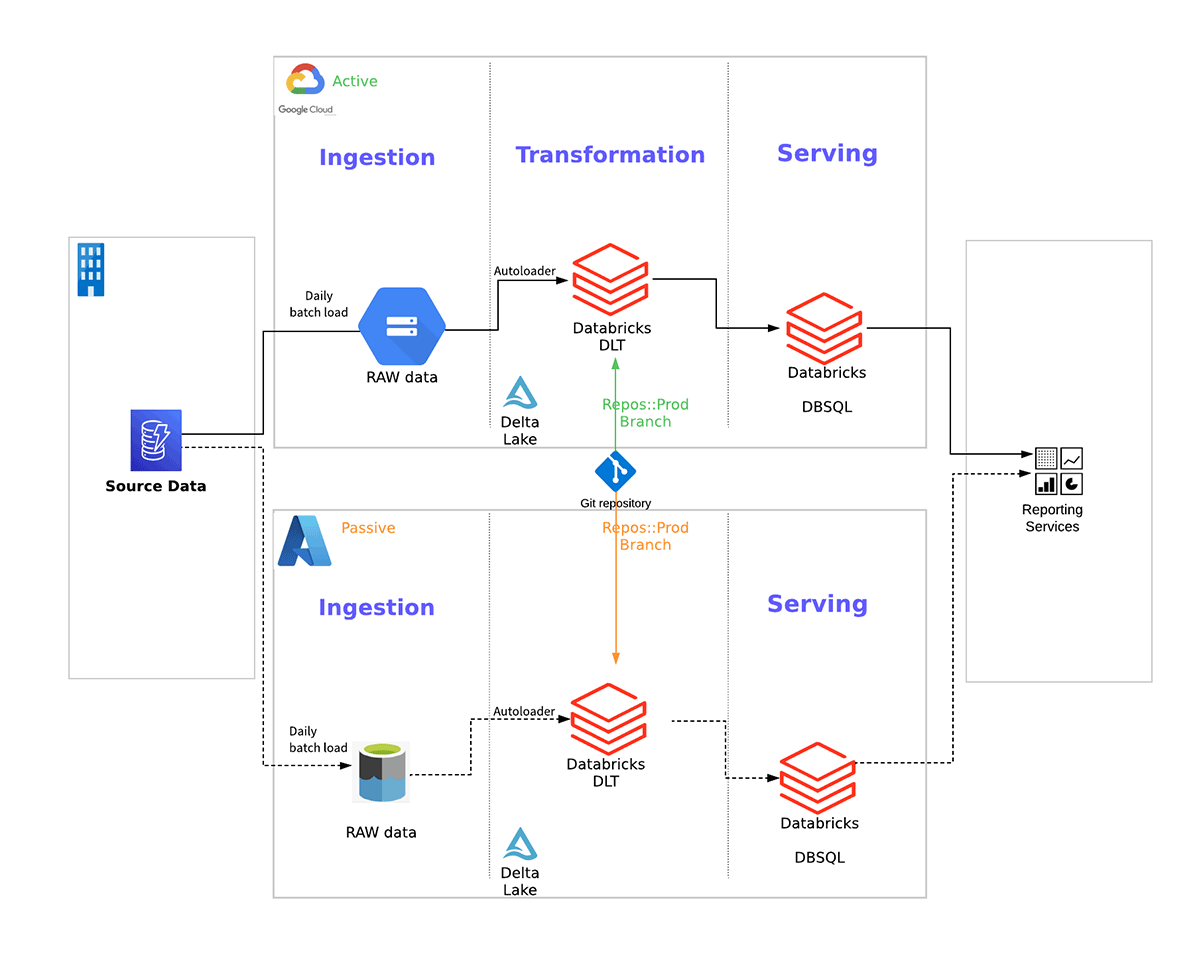
Below is an example of a multi-cloud solution for the General Ledger regulatory reporting services for a UK bank that leverages Databricks and follows the above blueprint. This approach allows the bank to meet their stressed-exit requirements while maintaining a single code base that is portable between the clouds:
Conclusion
Financial organizations wish to manage cloud vendor risk better, and in many cases, are required to adhere to regulatory requirements to execute on a stressed-exit strategy or manage data-locality requirements that vary by region. The combination of current and evolving regulatory requirements and managing the risk of vendor pricing models changing means that cloud portability for a hybrid cloud strategy is now an important item on the CIO and CTO’s agenda.
Databricks’ open-standards Lakehouse platform simplifies multi-cloud and hybrid cloud data architectures. Databricks allows organizations to develop and manage a single application that will run with the same functionality and optimized performance across all three of the major cloud vendors (Azure, AWS and GCP). Databrick’s core software stack is based on open-source code which allows hybrid operations for a single application which has on-premises (self-hosted) deployments as well as cloud vendor deployments.
The combination of application and data portability along with Databricks’ industry leading price/performance allows companies to reduce operating costs, simplify their architecture and meet their regulatory requirements.
To simplify secured deployment of Lakehouse with integrated industry best practices, unified governance and design patterns, you can also get started with Industry Blueprints.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Data Science and ML
October 1, 2024/10 min read
ICE/NYSE: Unlocking Financial Insights with a Custom Text-to-SQL Application
Product
November 27, 2024/6 min read
