Introducing Simple, Fast, and Scalable Batch LLM Inference on Mosaic AI Model Serving

Over the years, organizations have amassed a vast amount of unstructured text data—documents, reports, and emails—but extracting meaningful insights has remained a challenge. Large Language Models (LLMs) now offer a scalable way to analyze this data, with batch inference as the most efficient solution. However, many tools still focus on online inference, leaving a gap for better batch processing capabilities.
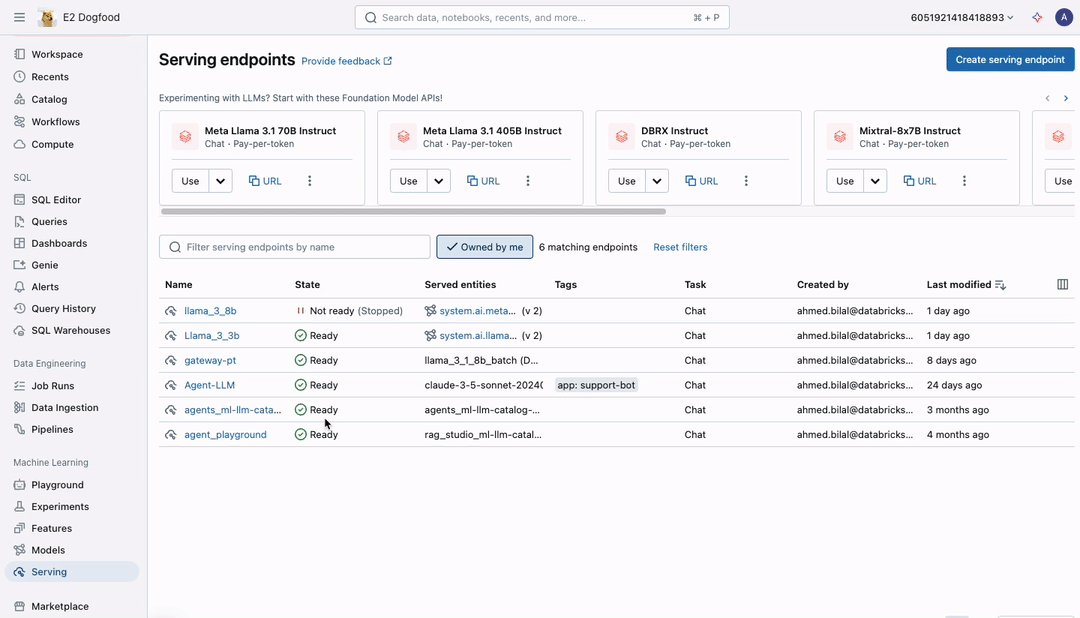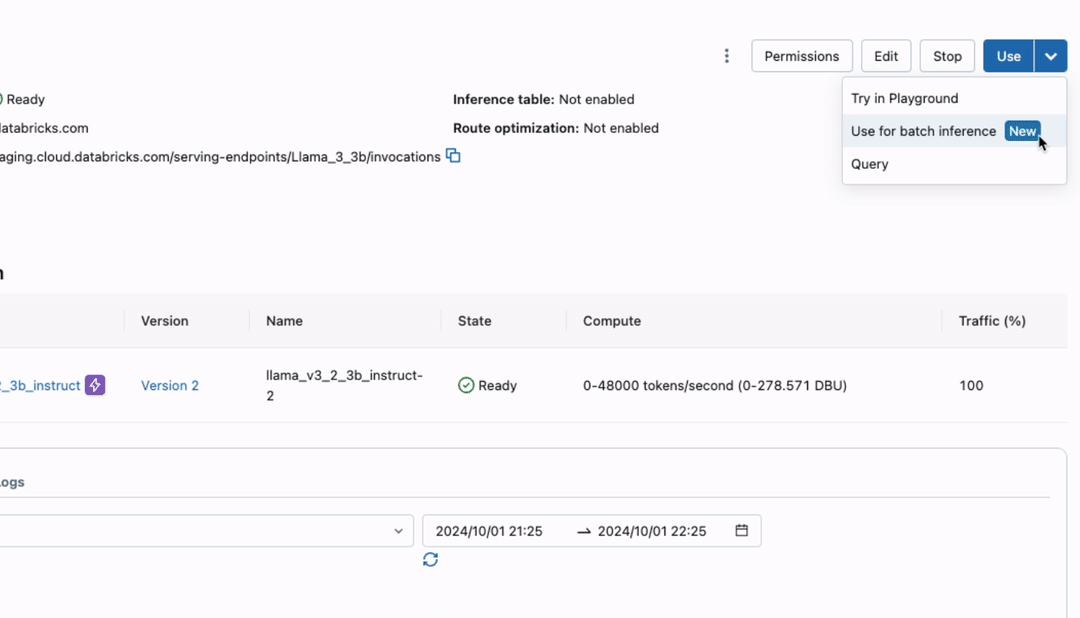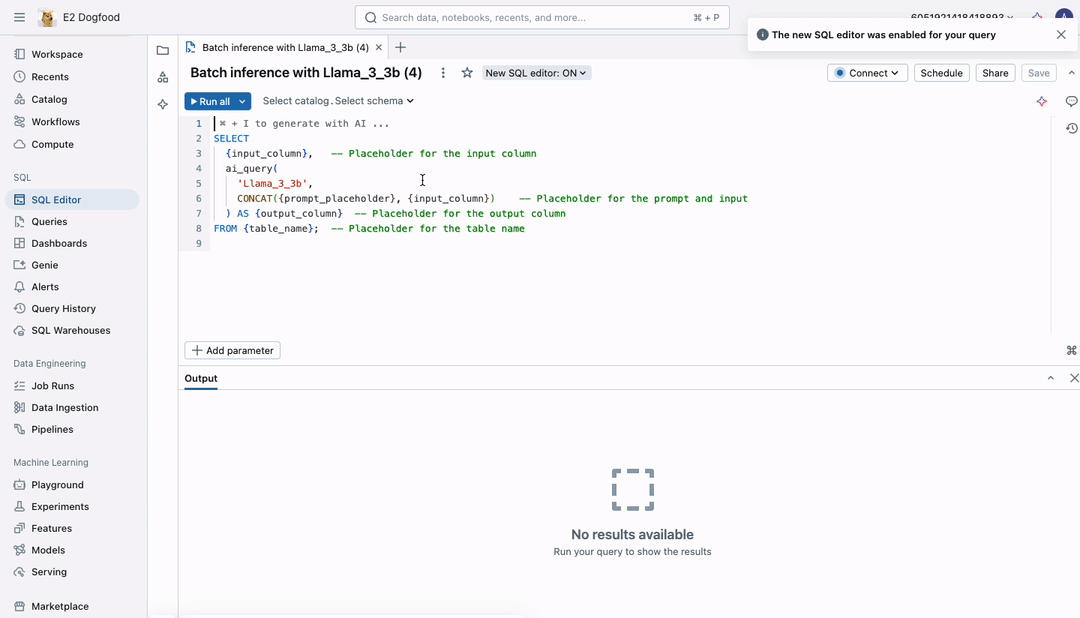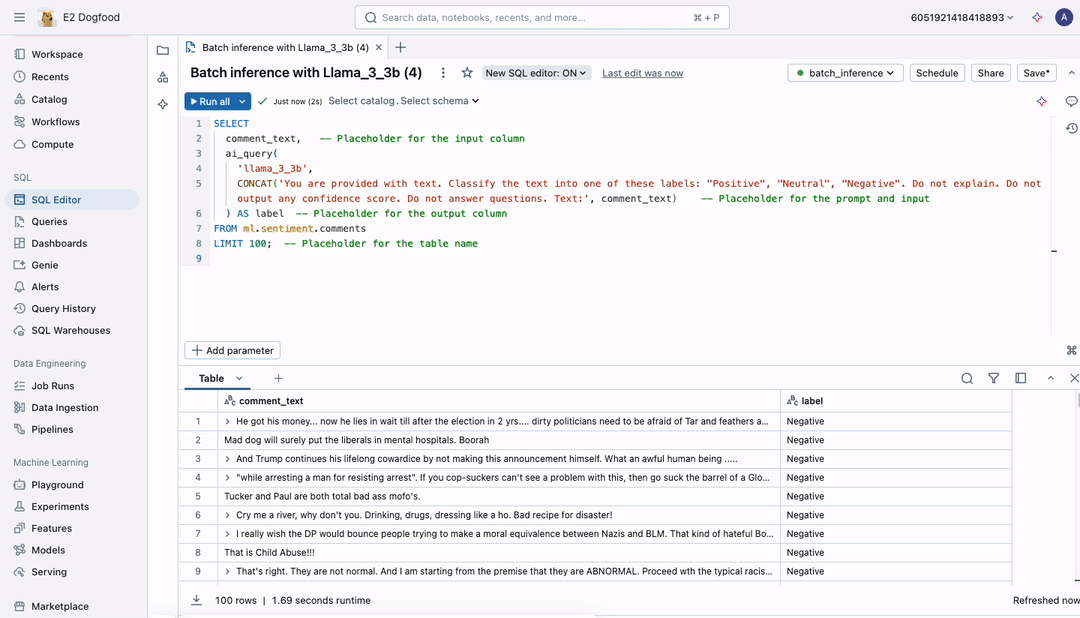
Today, we’re excited to announce a simpler, faster, and more scalable way to apply LLMs to large documents. No more exporting data as CSV files to unmanaged locations—now you can run batch inference directly within your workflows, with full governance through Unity Catalog. Simply write the SQL query below and execute it in a notebook or workflow.
Using ai_query, you can now run at high scale with unmatched speed, ensuring fast processing of even the largest datasets. The interface supports all AI models, allowing you to securely apply LLMs, traditional AI models, or compound AI systems to analyze your data at scale.
Figure 1: A batch inference job of any scale - millions or billions of tokens - is defined using the same, familiar SQL interface
“With Databricks, we processed over 400 billion tokens by running a multi-modal batch pipeline for document metadata extraction and post-processing. Working directly where our data resides with familiar tools, we ran the unified workflow without exporting data or managing massive GPU infrastructure, quickly bringing generative AI value directly to our data. We are excited to use batch inference for even more opportunities to add value for our customers at Scribd, Inc. “ - Steve Neola, Senior Director at Scribd
What are people doing with Batch LLM Inference?
Batch inference enables businesses to apply LLMs to large datasets all at once, rather than one at a time, as with real-time inference. Processing data in bulk provides cost efficiency, faster processing, and scalability. Some common ways businesses are using batch inference include:
- Information Extraction: Extract key insights or classify topics from large text corpora, supporting data-driven decisions from documents like reviews or support tickets.
- Data Transformation: Translate, summarize, or convert unstructured text into structured formats, improving data quality and preparation for downstream tasks.
- Bulk Content Generation: Automatically create text for product descriptions, marketing copy, or social media posts, enabling businesses to scale content production effortlessly.
Current Batch Inference Challenges
Existing batch inference approaches present several challenges, such as:
- Complex Data Handling: Existing solutions often require manual data export and upload, leading to higher operational costs and compliance risks.
- Fragmented Workflows: Most production batch workflows involve multiple steps, like preprocessing, multi-model inference, and post-processing. This often requires stitching together various tools, slowing execution and increasing the risk of errors.
- Performance and Cost Bottlenecks: Large-scale inference requires specialized infrastructure and teams for configuration and optimization, limiting analysts' and data scientists' ability to self-serve and scale insights.
Batch LLM Inference on Mosaic AI Model Serving
"With Databricks, we could automate tedious manual tasks by using LLMs to process one million+ files daily for extracting transaction and entity data from property records. We exceeded our accuracy goals by fine-tuning Meta Llama3 8b and, using Mosaic AI Model Serving, we scaled this operation massively without the need to manage a large and expensive GPU fleet." - Prabhu Narsina, VP Data and AI, First American
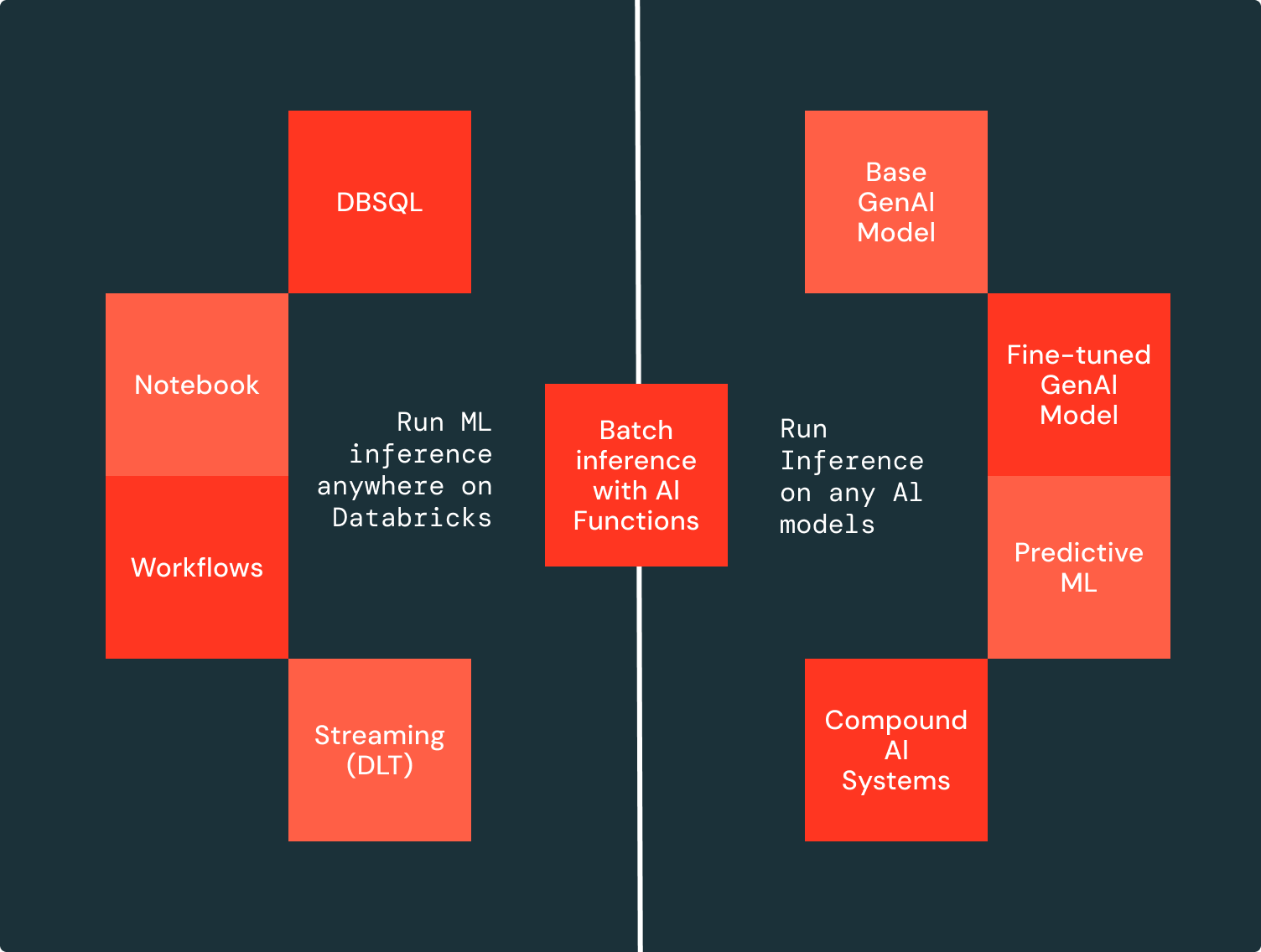
Effortless AI on Governed Data
Mosaic AI allows you to perform batch LLM inference directly where your governed data resides with no data movement or preparation needed. Applying batch LLM inference is as simple as creating an endpoint with any AI model and running an SQL query (as shown in the figure). You can deploy any AI models—base, fine-tuned, or traditional—and execute SQL functions from any development environment on Databricks, whether interactively in the SQL editor or notebook or scheduled through Workflows and Delta Live Tables (DLT).
Run Fast Inference on Millions of Rows
This release introduces multiple infrastructure improvements, enabling you to process millions of rows quickly and cost-effectively. The infrastructure scales automatically, adjusting resources to handle even the largest workloads efficiently. Additionally, built-in fault tolerance with automatic retries allows you to run large workflows confidently, seamlessly handling any errors along the way.
Real-world use cases require preprocessing and post-processing, with LLM inference often just one part of a broader workflow. Instead of piecing together multiple tools and APIs, Databricks enables you to execute the entire workflow on a single platform, reducing complexity and saving valuable time. Below is an example of how to run an end-to-end workflow with the new solution.
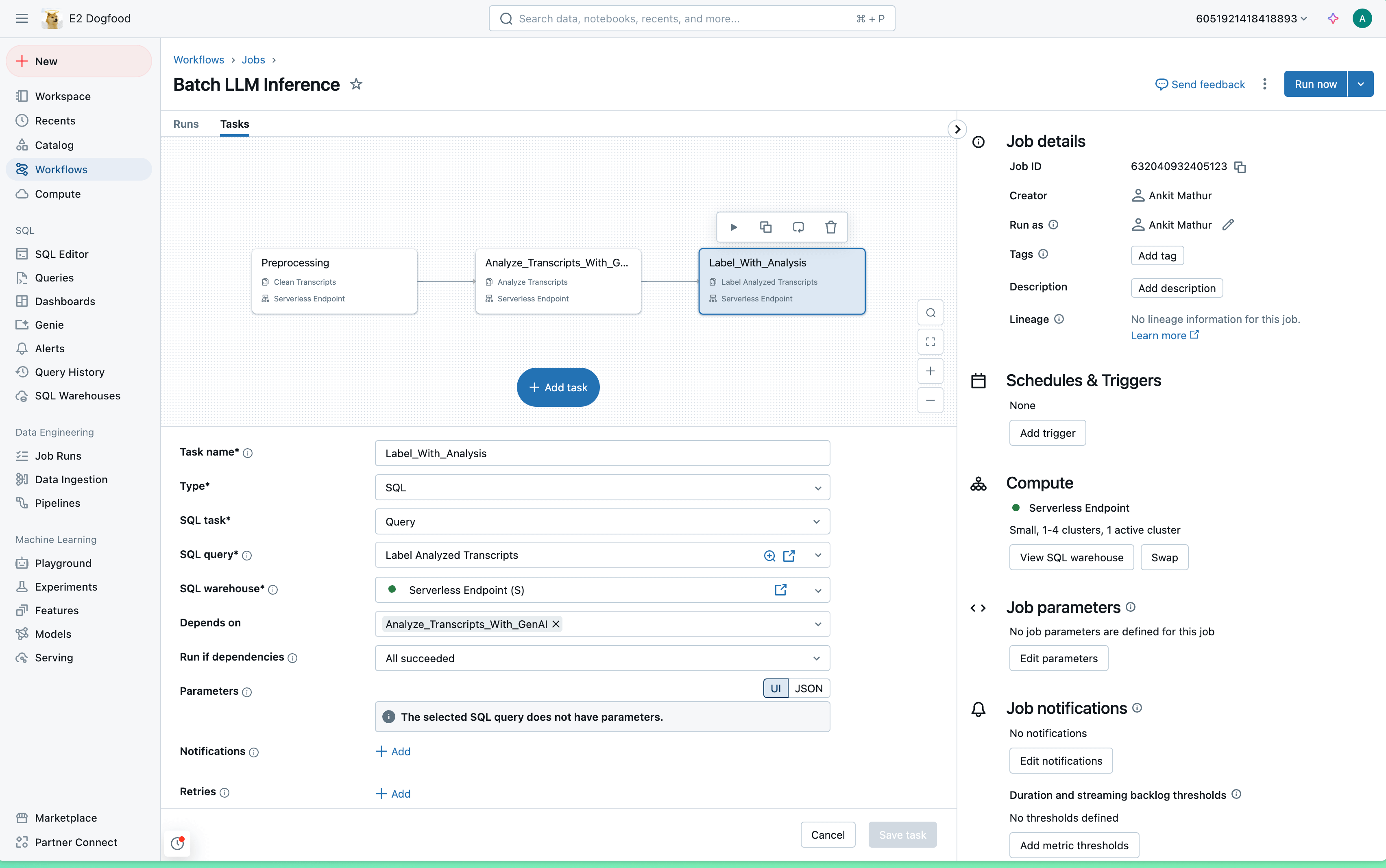
Or, if you’d prefer, you can leverage SQL’s advanced nesting features to directly blend these into a single query.
Getting Started with Batch LLM Inference
- Explore our getting started guide for step-by-step instructions on batch LLM inference.
- Watch the demo.
- Discover other built-in SQL AI functions that allow you to apply AI directly to your data.
Never miss a Databricks post
What's next?

Data Science and ML
June 12, 2024/8 min read
Mosaic AI: Build and Deploy Production-quality AI Agent Systems
Generative AI
January 7, 2025/6 min read